In building engineering and facade design, the use of thermally broken windows is widely regarded as one of the most effective strategies for improving overall thermal performance, indoor comfort, and long‑term building efficiency. Compared with conventional non‑broken aluminum frames, thermally broken systems integrate a non‑conductive barrier within the frame assembly to substantially reduce heat transfer, delivering measurable benefits across energy consumption, comfort, durability, and even condensation control.
Energy Performance and Operational Savings
One of the most compelling reasons thermally broken windows are considered worth the investment is their impact on energy efficiency. Traditional aluminum frames conduct heat readily due to aluminum’s high thermal conductivity, which can result in significant heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. The inclusion of a thermal break interrupts this continuous conductive path, lowering the frame’s U‑value—the metric for heat transfer—by 40–60 % or more compared to non‑broken frames. Lower U‑values directly translate to reduced demand on heating and cooling systems, resulting in lower energy bills and reduced HVAC loads over the lifetime of the building.
Thermally broken windows also contribute to peak heating and cooling load reduction, which is especially valuable in climates with wide temperature swings and for buildings with large glazed areas. By maintaining more stable interior temperatures, these systems reduce indoor climate fluctuations and improve the operational efficiency of building systems overall.
Indoor Comfort and Condensation Control
Thermally broken windows improve interior comfort by maintaining higher surface temperatures on interior frames, preventing “cold spots” in winter and overheating in summer. Additionally, thermal breaks reduce condensation formation , which is a common cause of mold growth, moisture damage, and degradation of nearby materials.
How Thermal Breaks Enhance Indoor Quality:
Minimize cold drafts near window frames.
Maintain more consistent indoor temperatures.
Reduce interior surface moisture and associated problems.
Acoustic and Long-Term Benefits
Thermal breaks also contribute to noise reduction by interrupting vibrational pathways in aluminum frames. This can significantly improve occupant comfort in urban or high-traffic environments.
From a lifecycle perspective, thermally broken systems deliver lower maintenance requirements . Because high-quality thermal break materials resist deformation, UV damage, and chemical degradation, they maintain performance for decades, minimizing the need for repairs or replacements.
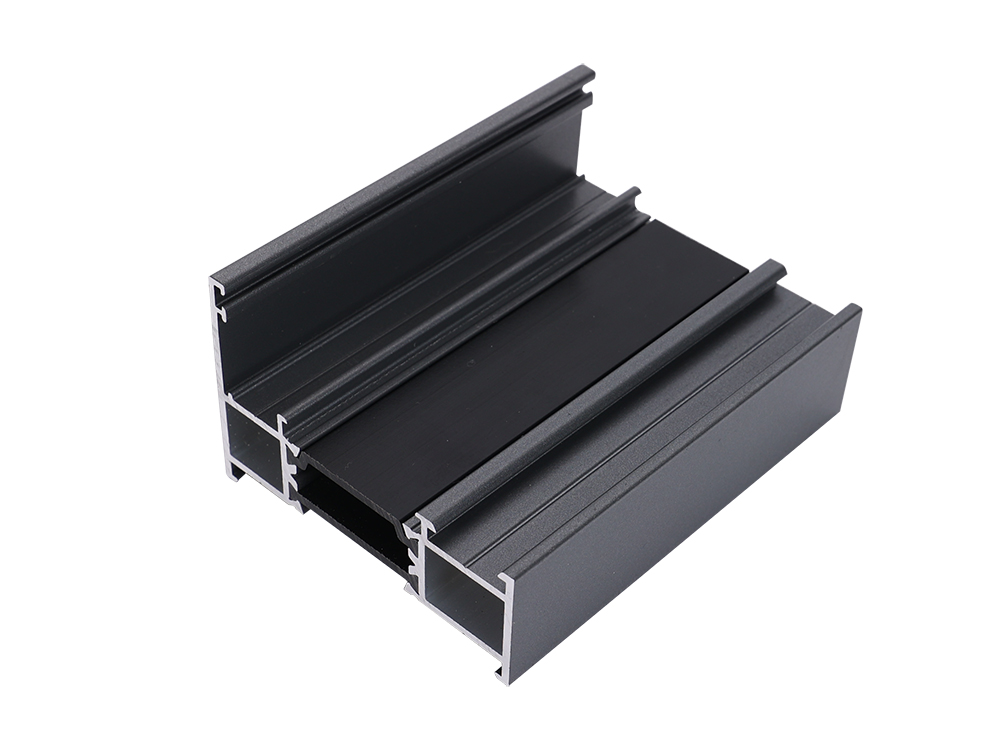

Integrating Advanced Thermal Break Materials
Products such as Bergman Thermal Break Strips enhance the performance of thermally broken windows and curtain walls. These nylon-based strips are engineered to:
Interrupt heat conduction through aluminum profiles.
Maintain structural integrity , supporting frame strength under load.
Provide adaptable dimensions , customizable in width, thickness, and length.
Improve condensation and moisture control , reducing maintenance issues.
Our Thermal Break Strip Features:
Material: Nylon, eco-friendly
Certifications: CE, ISO9001
Application: Windows, doors, curtain walls
Warranty: 5 years or more
By integrating these strips, engineers can achieve optimized thermal performance without compromising mechanical stability , aligning with sustainable building practices and energy efficiency regulations.
Although thermally broken windows often have higher initial costs compared with conventional aluminum frames, their benefits far outweigh the upfront investment . Reduced energy consumption, improved indoor comfort, lower maintenance, and long-term durability make them a cost-effective solution over a building’s lifecycle. With high-performance products like Bergman Thermal Break Strips , architects and engineers can ensure that windows and curtain walls deliver reliable insulation, structural stability, and sustainable performance for decades.